In the evolving world of artificial intelligence (AI) and automation, two terms frequently emerge: Computer Vision (CV) and Machine Vision (MV). While they are closely related, they are not the same. They are often used interchangeably, but they represent distinct yet interconnected fields of technology. Both involve processing and analyzing visual data, but their applications, scope, and underlying methodologies set them apart. If you’ve ever been confused about how they differ, you’re not alone. Let’s break it down in a simple way.
What is Computer Vision?
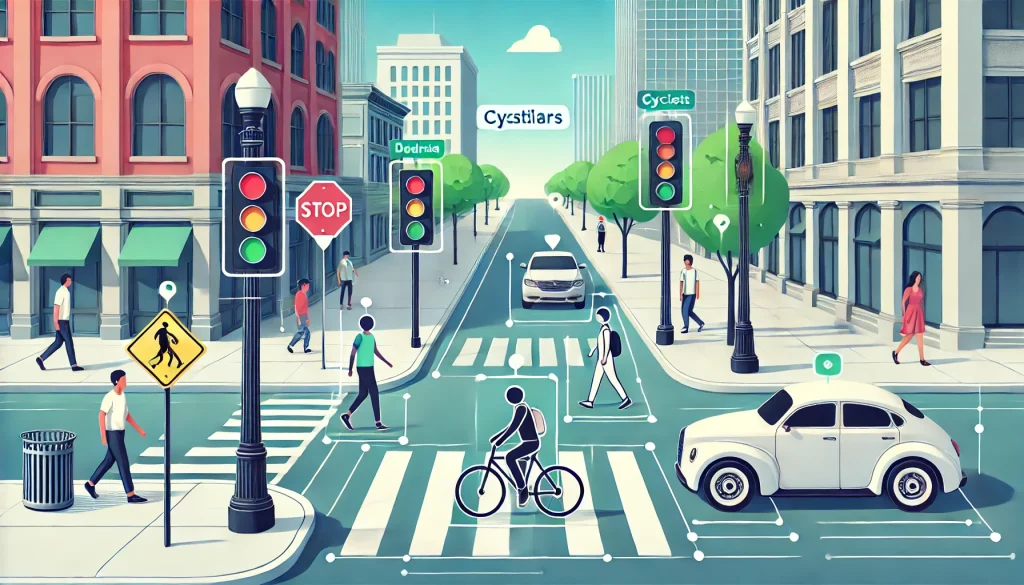
Computer Vision (CV) is a branch of artificial intelligence that enables machines to interpret and understand visual data from the world around them. It mimics human vision by analyzing images, videos, and 3D data to extract meaningful information and make intelligent decisions. Unlike machine vision, which is task-specific and used in controlled industrial environments, computer vision is more flexible and can be applied across various industries, from healthcare to autonomous vehicles.

How Does Computer Vision Work?
Computer vision relies on advanced algorithms, deep learning, and neural networks to process and analyze visual inputs. Some core techniques include:
- Image Classification – Identifying objects in an image (e.g., recognizing animals, vehicles, or faces).
- Object Detection – Locating and labelling multiple objects in an image or video.
- Facial Recognition – Identifying individuals based on facial features.
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR) – Converting printed or handwritten text into digital format.
- Edge Detection & Segmentation – Identifying shapes, contours, and objects within an image.
Where is Computer Vision Used?
Computer vision has widespread applications across multiple industries:
- Healthcare – Analyzing X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans for disease detection.
- Autonomous Vehicles – Identifying pedestrians, road signs, and obstacles.
- Retail – Automated checkout systems and customer behaviour analysis.
- Security & Surveillance – Facial recognition and anomaly detection.
- Augmented Reality (AR) & Virtual Reality (VR) – Real-time object tracking for immersive experiences.
Why is Computer Vision Important?
Computer vision is adaptive and intelligent, capable of evolving with new data and improving decision-making over time. It enhances automation, efficiency, and human-like perception in AI-powered systems, making it a foundational technology in modern AI applications.
Now that we’ve explored machine vision and computer vision, let’s compare them directly to highlight their key differences.
What is machine vision?
Machine Vision (MV) is a specialized field of automation that enables machines to capture, analyze, and interpret visual data for industrial applications. Unlike computer vision, which focuses on broader AI-driven perception, machine vision is designed for structured, high-speed, and highly accurate inspection and quality control processes in manufacturing and production environments.
How Does Machine Vision Work?
A machine vision system typically consists of the following components:
- Cameras & Sensors – Capture high-resolution images of objects or products.
- Lighting Systems – Ensure optimal illumination for image clarity.
- Processing Unit – Uses specialized algorithms to analyze images and detect defects, measure dimensions, or verify product assembly.
- Actuators & Robots – Trigger automated responses such as rejecting faulty products or adjusting production processes.
Where is Machine Vision Used?
Machine vision plays a critical role in industries where precision and efficiency are crucial. Common applications include:
- Manufacturing: Detecting defects, measuring dimensions, and ensuring proper assembly.
- Pharmaceuticals: Verifying packaging, labels, and expiration dates.
- Electronics: Inspecting circuit boards for soldering errors.
- Automotive: Ensuring proper alignment and part placement.
- Food & Beverage: Sorting, grading, and quality control.
Why is Machine Vision Important?
Machine vision improves accuracy, consistency, and efficiency in industrial settings by reducing human error, speeding up inspection processes, and enhancing product quality. It is task-specific and operates in controlled environments, making it a key enabler of Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing.
Looking for advanced Computer Vision and Machine Vision solutions? Check out Computer Vision & Machine Vision Services for AI-powered automation and quality control.
Here’s a quick breakdown of their differences:
| Feature | Computer Vision (CV) | Machine Vision (MV) |
|---|---|---|
| Focus Area | Broad AI-driven perception and recognition tasks. | Task-specific, focused on structured industrial environments. |
| Technology Used | Deep learning, neural networks, image processing. | Image processing algorithms, specialized sensors, lighting. |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, adaptable to various industries. | Limited to controlled environments for precision tasks. |
| Key Components | Cameras, deep learning models, GPUs, cloud-based processing. | Cameras, lighting, processing unit, actuators, robots. |
| Processing Approach | Generalized AI processing that evolves with new data. | Fixed processing based on predefined rules. |
| Applications | Image classification, object detection, facial recognition, OCR, AR/VR. | Defect detection, measurement, assembly verification, barcode scanning. |
| Industries | Healthcare, autonomous vehicles, retail, security, AR/VR. | Manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, electronics, automotive. |
Summary
Computer Vision (CV) is AI-driven, adaptive, and used across multiple fields to enhance automation, decision-making, and perception. While Machine Vision (MV) is task-specific, used in industrial settings for precision inspection and quality control. Both are essential for advancing automation and AI, and choosing the right one depends on the application needs.

